2021.05.20, 2020.09.21
1. What is Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes (ECK)
- Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes automates the deployment, provisioning, management, and orchestration of Elasticsearch, Kibana and APM Server on Kubernetes based on the operator pattern.
- Supported versions (ECK 1.4.1)
✓ kubectl 1.11+
✓ Kubernetes 1.12+ or OpenShift 3.11+
✓ Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), and Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
✓ Elasticsearch, Kibana, APM Server: 6.8+, 7.1+
✓ Enterprise Search: 7.7+
✓ Beats: 7.0+
- Subscription (https://www.elastic.co/kr/subscriptions)
✓ Subscription 종류: 오픈소스, 기본(free), 골드, 플래티넘, Enterprise
✓ 오픈소스 주요 지원 범위:
Filebeat, Metricbeat, Uptime 모니터(Heartbeat), Kibana Uptime 대시보드, 등등
✓ 기본(영구 무료) 주요 지원 범위:
Enterprise(유료) 구독을 통해 필드와 문서 수준의 액세스 제어, 머신 러닝, 그래프 분석 등과 같은 고급 기능과 함께 클러스터를 배포할 수 있는 역량 등 추가 기능을 제공
- References
https://github.com/elastic/cloud-on-k8s
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/cloud-on-k8s/current/k8s-quickstart.html
2. Installing ECK
- Environments (2021.05.20)
ECK 1.4.1, Elasticsearch/Kibana 7.12.1, kubernetes 1.16.15
- Environments (2020.09.21)
ECK 1.2.1, Elasticsearch/Kibana 7.9.1, kubernetes 1.16.15
- Deploy ECK in your kubernetes cluster
$ kubectl apply -f https://download.elastic.co/downloads/eck/1.4.1/all-in-one.yaml
$ kubectl -n elastic-system logs -f statefulset.apps/elastic-operator
3. Creating Elasticsearch cluster
a. Deploy an Elasticsearch cluster
- Before you deploy and run ECK, take some time to look at the basic and advanced settings available on this page. These settings are related both to Elasticsearch and Kubernetes.
$ kubectl create ns elastic-cluster
$ vi elasticsearch-emo-dev.yaml
apiVersion: elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co/v1
kind: Elasticsearch
metadata:
name: emo-dev
namespace: elastic-cluster
spec:
version: 7.12.1
nodeSets:
- name: master-nodes
count: 3
config:
node.roles: ["master"]
podTemplate:
spec:
initContainers:
- command:
- sh
- -c
- sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144
name: set-max-map-count
securityContext:
privileged: true
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: elasticsearch-data
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi
- name: data-nodes
count: 5
config:
node.roles: ["data"]
podTemplate:
spec:
initContainers:
- command:
- sh
- -c
- sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144
name: set-max-map-count
securityContext:
privileged: true
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: elasticsearch-data
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 100Gi
http:
tls:
selfSignedCertificate:
disabled: true # http service
# subjectAltNames: # https service
# - ip: 14.52.244.134
# - ip: 14.52.244.135
# - ip: 14.52.244.207
$ kubectl apply -f elasticsearch-emo-dev.yaml -n elastic-cluster
$ kubectl get elasticsearch -n elastic-cluster | egrep 'NAME|emo-dev'
NAME HEALTH NODES VERSION PHASE AGE
emo-dev green 8 7.12.1 Ready 10m
$ kubectl get pods --selector='elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co/cluster-name=emo-dev' -n elastic-cluster
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
emo-dev-es-data-nodes-0 1/1 Running 0 8m16s
emo-dev-es-data-nodes-1 1/1 Running 0 7m24s
emo-dev-es-data-nodes-2 1/1 Running 0 6m39s
emo-dev-es-data-nodes-3 1/1 Running 0 5m23s
emo-dev-es-data-nodes-4 1/1 Running 0 4m17s
emo-dev-es-master-nodes-0 1/1 Running 0 10m
emo-dev-es-master-nodes-1 1/1 Running 0 10m
emo-dev-es-master-nodes-2 1/1 Running 0 9m5s
$ kubectl patch service emo-dev-es-http -n elastic-cluster -p '{ "spec": { "type": "NodePort" } }'
$ k get svc -n elastic-cluster | egrep "NAME|emo-dev"
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
emo-dev-es-default ClusterIP None <none> 9200/TCP 10m
emo-dev-es-http NodePort 10.102.83.1 <none> 9200:31600/TCP 9m15s
emo-dev-es-transport ClusterIP None <none> 9300/TCP 10m
$
b. Request Elasticsearch access
- http
$ PASSWORD=$(kubectl get secret emo-dev-es-elastic-user -n elastic-cluster -o go-template='{{.data.elastic | base64decode}}')
$ IP=$(kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath='{.items[*].status.addresses[?(@.type=="InternalIP")].address}' | cut -d' ' -f 1)
$ PORT=$(kubectl get service emo-dev-es-http -n elastic-cluster --output jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="http")].nodePort}')
$ curl -u "elastic:$PASSWORD" "http://$IP:$PORT"
{
"name" : "emo-dev-es-master-nodes-2",
"cluster_name" : "emo-dev",
"cluster_uuid" : "r3k7qgAFQGKkADQ0AIlZhQ",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.12.1",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "docker",
"build_hash" : "3186837139b9c6b6d23c3200870651f10d3343b7",
"build_date" : "2021-04-20T20:56:39.040728659Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.8.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
$- https
$ PASSWORD=$(kubectl get secret emo-dev-es-elastic-user -n elastic-cluster -o go-template='{{.data.elastic | base64decode}}')
$ IP=$(kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath='{.items[*].status.addresses[?(@.type=="InternalIP")].address}' | cut -d' ' -f 1)
$ PORT=$(kubectl get service emo-dev-es-http -n elastic-cluster --output jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="https")].nodePort}')
$ kubectl get secret "emo-dev-es-http-certs-public" -o go-template='{{index .data "tls.crt" | base64decode }}' -n elastic-cluster > tls.crt
$ curl --cacert tls.crt -u "elastic:$PASSWORD" "https://$IP:$PORT"
$ curl --cacert tls.crt -u "elastic:$PASSWORD" "https://emo-dev-es-http:$PORT" --resolve emo-dev-es-http:$PORT:$IP
$ curl -u "elastic:$PASSWORD" -k "https://$IP:$PORT"
c. Deploy a Kibana Instance
$ vi kibana-emo-dev.yaml
apiVersion: kibana.k8s.elastic.co/v1
kind: Kibana
metadata:
name: emo-dev
spec:
version: 7.12.1
count: 3
elasticsearchRef:
name: emo-dev
http:
tls:
selfSignedCertificate:
disabled: true
$ kubectl apply -f kibana-emo-dev.yaml -n elastic-cluster
$ kubectl get kibana -n elastic-cluster
NAME HEALTH NODES VERSION AGE
emo-dev green 1 7.12.1 12m
$ kubectl patch service emo-dev-kb-http -n elastic-cluster -p '{ "spec": { "type": "NodePort" } }'
$ kubectl get svc -n elastic-cluster | egrep "NAME|emo-dev-kb-http"
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
emo-dev-kb-http NodePort 10.99.52.250 <none> 5601:31078/TCP 13m
$
d. Access Kibana
- URL
✓ IP : $ kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath='{.items[*].status.addresses[?(@.type=="InternalIP")].address}' | cut -d' ' -f 1
✓ Port : $ kubectl get service emo-dev-kb-http -n elastic-cluster --output jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="http")].nodePort}'
✓ Username: elastic (super user)
✓ Password : $ kubectl get secret emo-dev-es-elastic-user -o=jsonpath='{.data.elastic}' -n elastic-cluster | base64 --decode; echo

e. Creating user
- Menu
Home >> Management >> Stack Management >> Security >> User >> Create user

- Create user
Username: emo
Password: emo12#$
Roles: superuser
- Login to Kibana

- Request Elasticsearch access
$ IP=$(kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath='{.items[*].status.addresses[?(@.type=="InternalIP")].address}' | cut -d' ' -f 1)
$ PORT=$(kubectl get service emo-dev-es-http -n elastic-cluster --output jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="http")].nodePort}')
$ curl -u "emo:emo12#$" "http://$IP:$PORT"
4. Using Elasticsearch
a. 인덱스/샤드란 무엇인가?
- https://esbook.kimjmin.net/03-cluster/3.2-index-and-shards
- 인덱스 / 샤드 / 세그먼트
Elasticsearch에 저장된 데이터는 인덱스, 각 인덱스는 다수의 샤드로, 샤드는 다수의 세그먼트로 구성

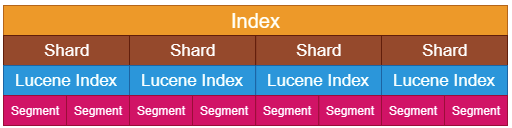
- 인덱스(Index)
Elasticsearch에서는 단일 데이터 단위를 도큐먼트(document)라고 하며 이 도큐먼트를 모아놓은 집합
인덱스는 기본적으로 샤드(shard)라는 단위로 분리되고 각 노드에 분산되어 저장, 샤드는 루씬의 단일 검색 인스턴스

- 샤드 (shard)
샤드는 루씬 인덱스이며, 인덱싱을 하거나 데이터 일부를 조회하기 위한 독립적인 검색 엔진
각 쿼리나 집계가 샤드당 단일 스레드로 실행되기 때문에, 최소 쿼리 지연 시간은 통상적으로 샤드 크기에 의존
- Primary shard / replica
처음 생성된 샤드를 프라이머리 샤드(Primary Shard), 복제본은 리플리카(Replica)라고 부릅

프라이머리 샤드 수는 인덱스를 처음 생성할 때 지정하며, 인덱스를 재색인 하지 않는 이상 바꿀 수 없음
b. Using ILM (Index Lifecycle Management)
b-1. hot-warm 아키텍처
- 동일(uniform) 또는 균일(homogenous) 클러스터 아키텍처
모든 데이터 노드가 동일한 사양을 가지며 모든 역할을 처리, 색인과 쿼리 작업 부하를 균등하게 공유
- hot-warm 아키텍처

✓ hot 데이터 노드는 최신 인덱스들을 저장하며, 모든 색인 부하를 처리, CPU와 I/O 집약적, SDD 사용
✓ warm 데이터 노드는 읽기 전용 인덱스의 장기간 저장, CPU와 Memory 집약적, Local HDD or SAN 사용
✓ 로그와 메트릭 같은 시계열 데이터 작업을 할 때 특히 인기
✓ 데이터가 일반적으로 변경이 불가능하고 시계열 기반 인덱스로 색인된다는 원칙
✓ ILM(Index Lifecycle Management)을 사용하여 hot-warm-cold 아키텍처를 구현
Lifecycle : hot > warm (shrink, force merge) > cold (freeze) > delete
Hot-Warm-Cold는 설정되어 있지 않음, Roll over는 기본 설정되어 있음
Beat(Filebeat, Metricbeat, Heatbeat)와 Logstash에서 생성하는 Index는 기본적으로 ILM 설정이 활성화되어 있음
b-2. 저장 공간 고려사항
- 매핑의 최적화
✓ 디스크에서 압축되는 정도에 영향을 미침, Beat와 Logstash는 최적화되어 제공
✓ 동적으로 문자열을 매핑할 때, 기본 동작은 풀 텍스트 검색에 사용되는 text와 Kibana에서 데이터를 집계시 사용되는 keyword 양쪽으로 데이터를 매핑 (불필요할 경우 제외)
- 샤드 크기를 가능한 한 크게 유지
✓ 각 샤드에는 약간의 힙 공간을 사용하는 오버헤드가 존재 (샤드 수가 증가하면 오버헤드 공간도 증가됨)
✓ 장기간 보존을 위한 평균 샤드 크기를 20GB에서 50GB 사이로 유지 권장
✓ 각 샤드의 부하는 세그먼트 개수와 크기에 따라 결정 (forcemerge 기능을 사용하여 작은 세그먼트를 큰 세그먼트로 병합)
✓ 노드에 설정한 힙 1GB 당 샤드 20개 정도가 적당 (Default heap size: 2GB)
- 저장 공간 볼륨 튜닝
✓ JSON 소스를 효율적으로 압축하는 것은 디스크에서 데이터가 얼마큼의 공간을 차지할 것인지에 상당한 영향을 미침
✓ best_compression 코덱: 색인 동안 약 5-10%의 성능 저하, 디스크 공간 확보
b-3. 샤드 크기 관리
- 시간 기반 인덱스 (고정 시간 주기 관리, 예. 일)
- Rollover 및 Shrink API
✓ Rollover 인덱스 API: 도큐먼트와 인덱스의 개수를 지정 또는 도큐먼트의 최대 기간을 지정, 조건 만족 시 다운타임 없이 신규 인덱스 생성
✓ Shrink 인덱스 API: 기존 인덱스를 더 적은 개수의 프라이머리 샤드를 가진 신규 인덱스로 변경(shrink)
- Rollover 설정
✓ Stack Management > Index Lifecycle Policies in Kibana
metricbeat

Warm / Cold / Delete phase는 비 활성화되어 있음
✓ Stack Management > Index Management in Kibana

b-4. References:
- Elastic Cloud Elasticsearch Service에서 로깅과 메트릭을 위한 hot-warm 아키텍처 설정
- 인덱스 수명 주기 관리를 통해 Hot-Warm-Cold 아키텍처 구현
- 내가 운영하는 Elasticsearch 클러스터에 얼마나 많은 샤드가 필요할까?
https://www.elastic.co/kr/blog/how-many-shards-should-i-have-in-my-elasticsearch-cluster
c. Creating Index
- Index 생성 (Shard/Replica 설정)
Index가 있는 경우 에러 발생, Primary shard는 수정 불가하며 reindex시 변경 가능함
$ PASSWORD=$(kubectl get secret emo-dev-es-elastic-user -n elastic-cluster -o go-template='{{.data.elastic | base64decode}}')
$ IP=$(kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath='{.items[*].status.addresses[?(@.type=="InternalIP")].address}' | cut -d' ' -f 1)
$ PORT=$(kubectl get service emo-dev-es-http -n elastic-cluster --output jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="http")].nodePort}’)
$ curl -X PUT -u elastic:$PASSWORD http://$IP:$PORT/test?pretty -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"settings" : {
"index.number_of_shards": 50,
"index.number_of_replicas": 1
}
}
'
{
"acknowledged" : true,
"shards_acknowledged" : true,
"index" : "test"
}
$- Index별 Replica/Shard 설정 조회
$ curl -u elastic:$PASSWORD http://$IP:$PORT/test/_settings?pretty=true -s | egrep "number_of_shards|number_of_replicas"
"number_of_shards" : "50",
"number_of_replicas" : "1”,
$- Index별 Shard 현황 조회
$ curl -u elastic:$PASSWORD http://$IP:$PORT/_cat/shards/_all?pretty=true -s | grep test | sort
test 0 p STARTED 0 208b 10.244.9.79 observer-es-data-nodes-9
test 0 r STARTED 0 208b 10.244.8.100 observer-es-data-nodes-0
test 1 p STARTED 0 208b 10.244.8.100 observer-es-data-nodes-0
test 1 r STARTED 0 208b 10.244.8.101 observer-es-data-nodes-8
test 2 p STARTED 0 208b 10.244.8.101 observer-es-data-nodes-8
test 2 r STARTED 0 208b 10.244.6.72 observer-es-data-nodes-3
…or
Management > Stack Management > Index Management in kibana

'Kubernetes > NoSQL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| MongoDB Sharded by Bitnami (0) | 2021.11.03 |
|---|---|
| MongoDB Community Kubernetes Operator (1) | 2021.11.03 |
| Redis - corrupted cluster config file (0) | 2021.10.02 |
| Redis cluster (0) | 2021.09.22 |
| Elasticsearch - Index lifecycle error (0) | 2021.09.15 |



댓글